# 文档初探(八): Slot
# slot 的作用域
Vue.component("navigation-link", {
props: ["url"],
template: `
<a
:href="url"
>
子组件: Clicking here will send you to: {{ url }}
<br/>
<slot></slot>
</a>
`,
data() {
return {};
}
});
new Vue({
el: "#app",
template: `
<navigation-link url="https://baidu.com">
Logged in as {{ user }}
<br/>
父组件: Clicking here will send you to: {{ url }}
</navigation-link>
`,
data() {
return {
user: "wanmao"
};
}
});
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
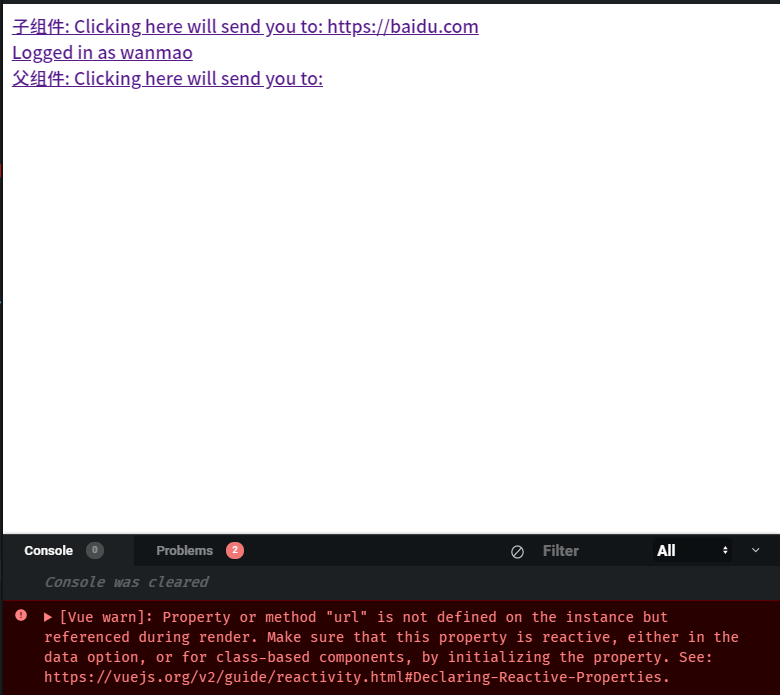
slot 只能得到和自己处于同一个 scope 里的数据. 上例中, 子组件里的url就是通过props传下来的, 所以能打印出结果, 父组件里user在data里, 所以也能打印出结果, 但是父组件的url没有在data里找到, 于是报错.
# fallback content
fallback content 为我们提供当 slot 的替换内容不存在时的解决方法, 在<slot></slot>里面写上 fallback content 即可.
Vue.component("navigation-link", {
props: ["url", "fallback"],
template: `
<a
:href="url"
>
子组件: Clicking here will send you to: {{ url }}
<br/>
<slot>{{fallback}}</slot>
</a>
`,
data() {
return {};
}
});
new Vue({
el: "#app",
template: `
<navigation-link url="https://baidu.com" :fallback="fallback">
</navigation-link>
`,
data() {
return {
user: "wanmao",
fallback: "This is fall back content"
};
}
});
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29

# named slots
我们在一个实例或者组件里同时使用到多个 slot 时, 可以将其命名, 从而更能快速且正确地将模板填充进去. 如果不对 slot 进行命名, 那么它就默认名为default.
Vue.component("base-layout", {
props: ["url", "fallback"],
template: `
<div class="container">
<header>
<slot name="header"></slot>
</header>
<main>
<slot></slot>
</main>
<footer>
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</footer>
</div>
`
});
new Vue({
el: "#app",
template: `
<base-layout>
<template v-slot:header>
<h1>Here might be a page title</h1>
</template>
<p>A paragraph for the main content.</p>
<p>And another one.</p>
<template v-slot:footer>
<p>Here's some contact info</p>
</template>
</base-layout>
`
});
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
v-slot也有简写的形式:
<template #header>
<h1>Here might be a page title</h1>
</template>
1
2
3
2
3
# scoped slots
scoped slots 与 named slots 区别在于, slots 里的内容是在 child scope 里而不是在 parent scope 里.
Vue.component("current-user", {
template: `
<span>
<slot :user="user">{{ user.lastName }}</slot>
</span>
`,
data() {
return {
user: {
firstName: "wan",
lastName: "fallback content"
}
};
}
});
new Vue({
el: "#app",
template: `
<current-user>
<template v-slot:default="slotProps">
{{slotProps.user.firstName}}
</template>
</current-user>
`
});
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
如果只有一个默认 slot, 我们可以略去template, 简写为:
<current-user v-slot:default="slotProps">
{{ slotProps.user.firstName }}
</current-user>
1
2
3
2
3
如果有多个 slot, 那么还是得使用template:
<current-user>
<template v-slot:default="slotProps">
{{ slotProps.user.firstName }}
</template>
<template v-slot:other="otherSlotProps">
...
</template>
</current-user>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 解构 slot props
我们也可以使用解构赋值来传递 slot:
<current-user v-slot="{ user }">
{{ user.firstName }}
</current-user>
1
2
3
2
3
使用解构同样可以使用v-slot的简写方式:
<current-user #default="{ user }"
><!--#后必须跟上slot的name属性, 默认是default -->
{{ user.firstName }}
</current-user>
1
2
3
4
2
3
4